Aurora Chains
Aurora Chains are dedicated EVM-compatible blockchains built on top of the NEAR Protocol. They are your own instance of Aurora – every Aurora Chain is based upon the Aurora smart contract, also called Aurora Engine. It provides you with a customized and dedicated blockchain environment.
Benefits include:
- No need for additional validators: when your Aurora Chain is deployed, it automatically gets all the Near Blockchain validators, which are above 300.
- Configuration: create whitelists, choose your own custom token, gas mechanics, integrate KYC, and much more.
- Complete ecosystem: the Rainbow Bridge, on-ramps, indexers, oracles, DEXes, etc., Aurora Cloud provides a selection of integrations that can be deployed to your chain in order to speed up development
- Focus on your business: the tech side of the integration and support are entirely on the Aurora Labs team's shoulders.
- Seamless interoperability with Aurora, Near, and any other Aurora Chains: you can freely move your assets using the Rainbow Bridge and call contracts via cross-contract calls (XCC). There is no disjointness in between. You can call any smart contract in any other Aurora Chain or NEAR and interact with them freely.
- Top-notch TPS: we can provide you dozens of millions of transactions daily for your ecosystem – 1k+ transactions per second.
What can be configured?
To make Aurora Chain work in the best possible way for your business, we will help you to configure your setup. Among the features to configure are:
- Base token of your Aurora Chain.
- Gas mechanics within your chain, such as fixed fee or percentage-based fees, gasless transactions, paying for gas with a custom token, etc.
- Permission levels: whitelist usage - who can transact or deploy contracts? You can learn about how to operate Aurora Chain Whitelists from your dApp here.
- Private chain: can be built using a private NEAR shard Calimero.
How do I create my Aurora Chain?
To get an Aurora Chain for your business, please get in touch with the Aurora Labs team via the 'Contact Us' form on the Aurora Cloud website. We will schedule a call with you to determine the initial scope of your project in order to define the configuration of your Aurora Chain (e.g., public access, gas mechanics, token, services, whitelist usage). You will then get access to your chain and to the Aurora Cloud Console within a couple of days.
Once deployed, you can choose to enrich it with a selection of services you require (e.g., bridge configuration, oracles, on-ramps, block explorer, etc.) and start your development.
We will provide you with access to the Aurora Cloud Console to manage and monitor your chain. On the Aurora Chain Summary Page, you will be able to monitor chain statistics and performance:
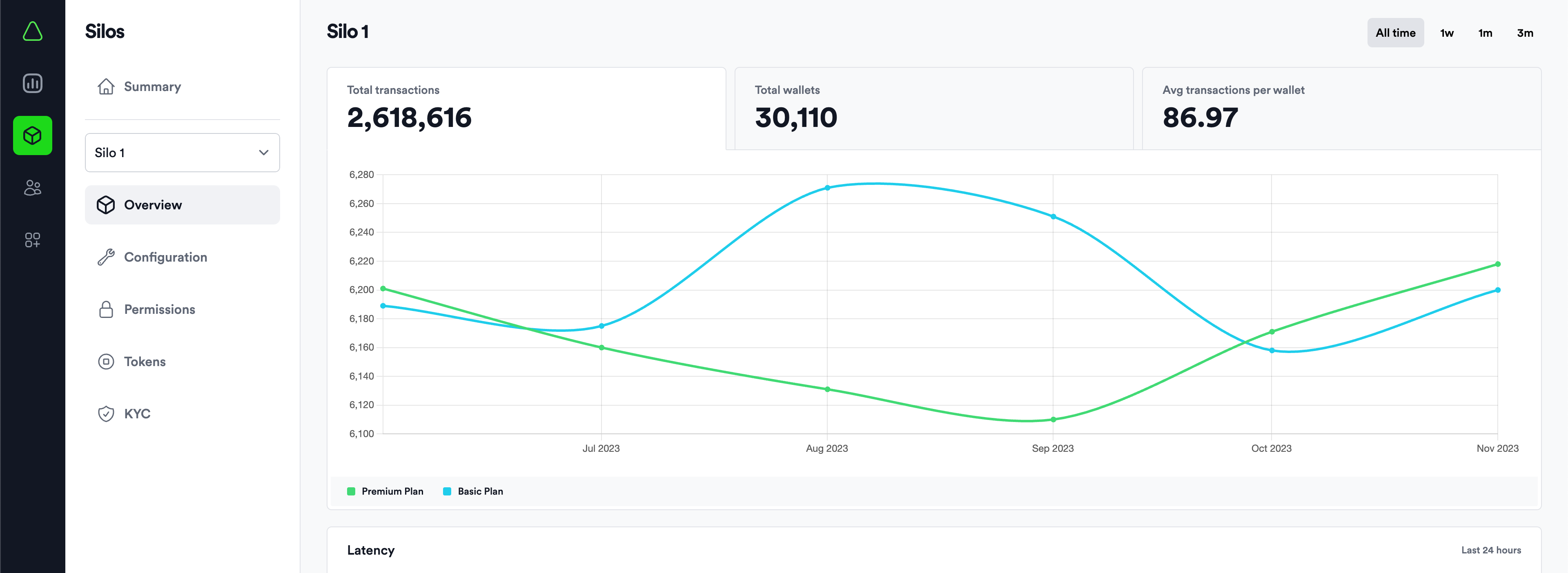
You can manage and track the information about the configured Aurora Chain with Aurora Cloud Console. The configuration page will provide you with all of the necessary details about your chain:
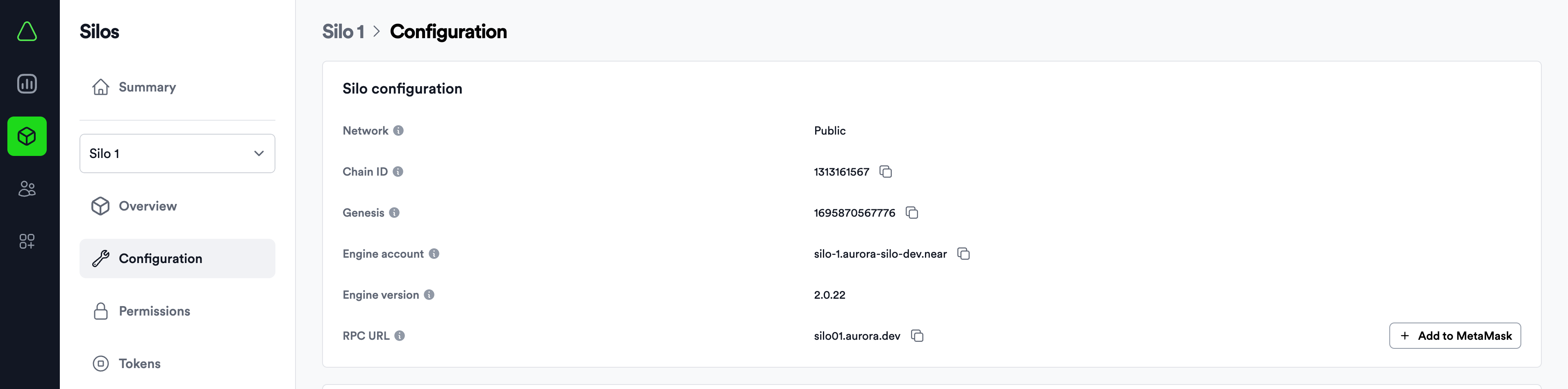
Note the RPC URL field above. As you can see, the RPC endpoint looks similar to the one Aurora Mainnet is using, and has a format like https://your-chain.aurora.dev.
Talking about the RPC nodes, we will provide a scalable cluster of those for you, accessible by that link. But if you want to manage RPCs by yourself, there are two options for you:
Either use our docker images on your instances. And run our optimized infrastructure on your hardware, with us supporting it.
Or create a Standalone RPC nodes by yourself and allow the community to scale the network. You can read more about spinning your own Aurora node in this DevPortal article.
Whitelist Management
Every Aurora Chain has two types of whitelists defining the level of permissions for your users:
- Transaction Access Whitelist: to enable user accounts (EOAs) to execute transactions in your chain.
- Deployment Access Whitelist: to enable EOAs to deploy contracts to your chain.
Both of them are optional. So, if you want to allow the usage and development for everyone, both of them will be disabled. If not, you will need to manage them. The easiest way will be to do this in the Aurora Cloud Console on the Aurora Chain Permissions Page:
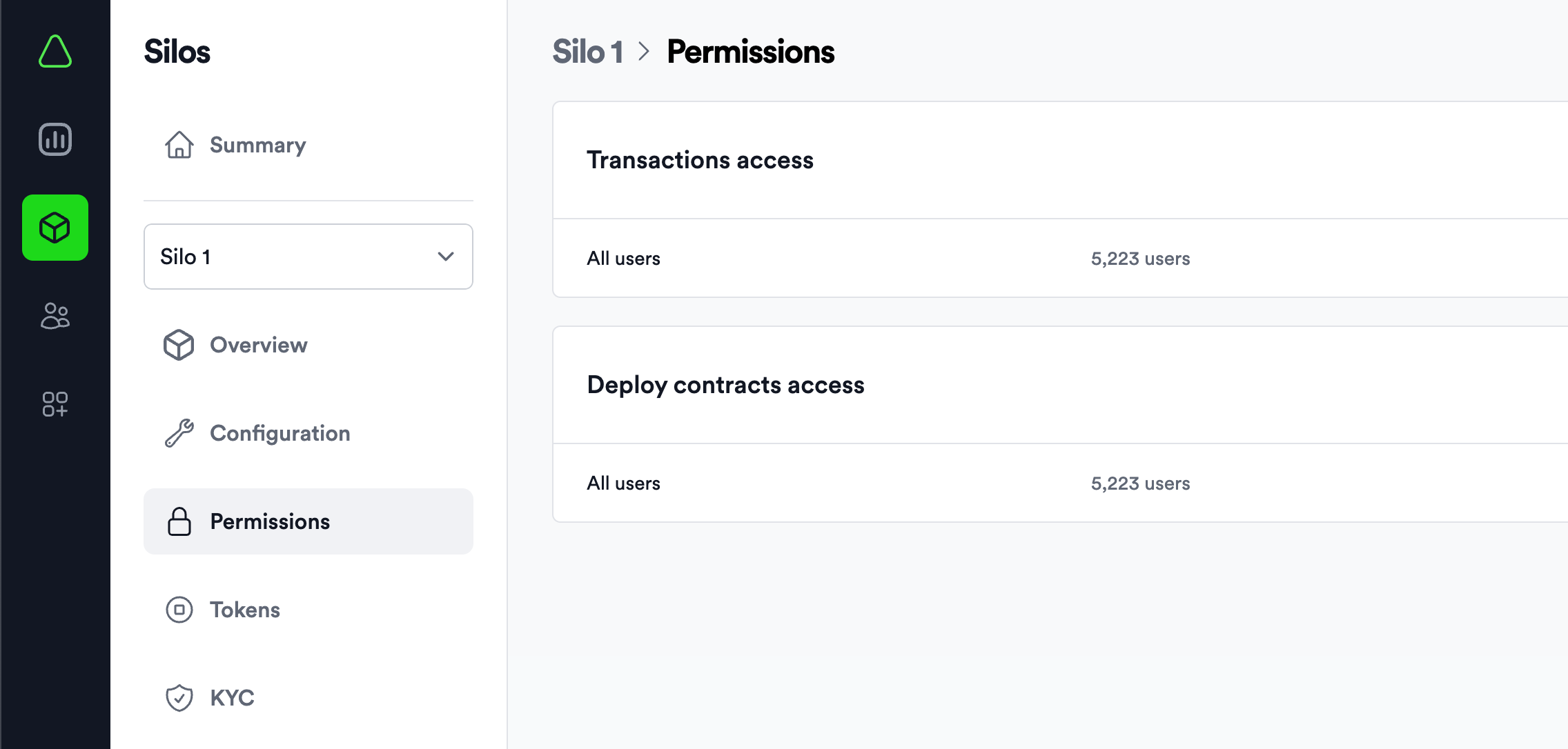
You can also manage them by using Cloud Console API, which is described in detail in the table below.
Note: you will still be able to do this via the direct contract calls on Near blockchain, if needed. But we discourage you from using those, because it is not as convenient as Cloud Console UI or Cloud Console API.
Aurora Cloud Console: Aurora Chain API
| API path | /chain/whitelists/ |
| method | POST |
| required request headers | Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Bearer [ACC API Token] |
| required request params | op_type: add_entry and remove_entry are supported kind: Type of whitelist. developer or user are supported. entry: EOA address to add or remove. |
| response code | On success: 200 OKOn Error: - 400 BadRequest: if a request body is empty or could not be parsed or a number of operations is greater than RequestConfig.MaxBatchLen- 401 Unauthorized: if authorization header does not satisfy the [conditions](401 Conditions)- 403 Forbidden: if a caller is [not authorized](403 Conditions) to perform all updates in request array (i.e., partial updates are not allowed)- 408 RequestTimeout: with partial response, if not all responses from storage node are received before RequestConfig.TimeoutMs or Timeout header in request- 500 InternalServerError: if fails to send an update request to the storage node, or fails to parse a response from the storage node |
| request example | |
| response example - success | |
| response examples - error | Response Code: 400 Bad Request |
Learn more
Here are some in-depth articles to discover details about how Aurora Chain works and how it has been developed:
Contact Us
If you feel your business could benefit from Aurora Cloud, please do not hesitate to contact us at hello@auroracloud.dev.